Entering the realm of the loan approval process, get ready for a deep dive into the stages, players, and crucial evaluation aspects that make or break the deal. It’s time to decode the secrets behind getting that coveted approval.
Let’s uncover the mystery of what it truly takes to navigate the loan approval process seamlessly and emerge victorious on the other side.
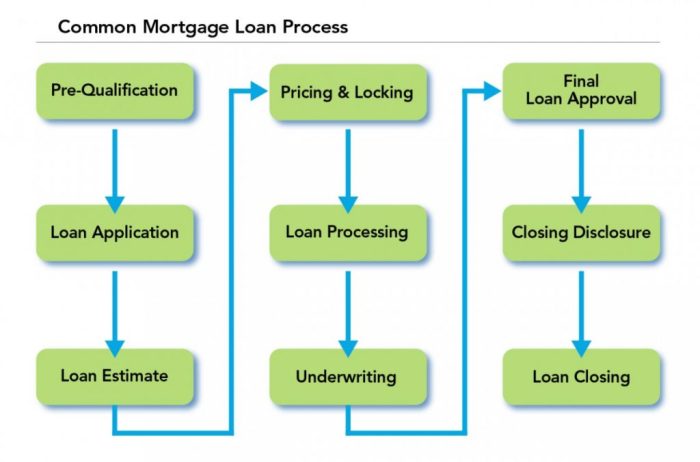
Overview of the Loan Approval Process
When it comes to getting that dough for your dreams, the loan approval process is the name of the game. It’s like a well-choreographed dance with multiple steps and players involved to make sure you’re fully prepared to take on that financial commitment.
Stages Involved in the Loan Approval Process
- Application: First things first, you gotta fill out that application form with all your deets.
- Verification: The lenders will then verify your info like income, credit score, and employment status to see if you’re a good bet.
- Underwriting: This is where the big decisions happen. The underwriters assess your risk level and determine if you’re approved or not.
- Approval: If all goes well, you’ll get that sweet approval and be one step closer to your financial goals.
- Closing: The final stage where all the paperwork is signed, and you officially get the funds in your account.
Key Players Involved in the Process
- Borrower: That’s you, the one looking to get that cash to make things happen.
- Lender: The financial institution or entity providing the funds for your loan.
- Underwriter: The person who crunches the numbers and makes the call on your approval status.
- Loan Officer: Your go-to person who guides you through the process and helps you with any questions.
Importance of a Thorough Evaluation During the Process
During the loan approval process, a thorough evaluation is crucial to ensure that both parties are making the right choice. It helps the lender assess the risk involved in lending you money and helps you understand your financial responsibilities. Remember, it’s not just about getting the loan approved but also about setting yourself up for success in the long run.
Documentation Required for Loan Approval
When applying for a loan, you need to gather a variety of documents to support your application. These documents are crucial for the approval process as they provide the lender with necessary information to assess your financial situation and determine your eligibility for the loan.
List of Commonly Required Documents
- Identification: A valid form of identification, such as a driver’s license or passport, is essential to verify your identity.
- Proof of Income: Documents like pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements are needed to demonstrate your ability to repay the loan.
- Credit History: Lenders will request your credit report to assess your creditworthiness and repayment history.
- Employment Verification: Proof of employment, such as a letter from your employer or recent pay stubs, helps confirm your stability and income source.
- Proof of Residence: Utility bills or a lease agreement can serve as proof of your current address.
- Asset Information: Documentation for any assets you own, like property deeds or investment statements, may be required for certain types of loans.
Tips for Organizing and Preparing Documents
- Start Early: Begin gathering all necessary documents as soon as you decide to apply for a loan to avoid any last-minute rush.
- Create a Checklist: Make a list of all required documents and check them off as you collect each one to ensure you have everything needed.
- Organize in a Folder: Keep all your documents neatly organized in a folder or binder to easily access them when submitting your loan application.
- Make Copies: Have copies of all documents in case the lender requests additional information or if any paperwork gets misplaced.
- Review for Accuracy: Double-check all documents for accuracy and completeness to prevent delays in the approval process.
Credit Score and its Impact: Loan Approval Process
Credit scores play a crucial role in the loan approval process. Lenders use credit scores to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and determine the level of risk associated with lending them money. A higher credit score typically indicates responsible financial behavior and can increase the likelihood of loan approval. On the other hand, a low credit score may result in higher interest rates or even rejection of the loan application.
Ways to Improve Credit Score
- Pay bills on time: Timely payment of bills demonstrates reliability and can positively impact your credit score.
- Reduce credit card balances: Keeping credit card balances low relative to the credit limit can improve your credit score.
- Limit new credit applications: Multiple credit inquiries within a short period can lower your credit score, so it’s important to be selective when applying for new credit.
- Monitor your credit report: Regularly checking your credit report for errors and addressing any discrepancies can help maintain a healthy credit score.
Credit Score Requirements for Different Loans
| Loan Type | Credit Score Requirement |
|---|---|
| Mortgage | Generally, a credit score of 620 or higher is required for conventional mortgages, but some lenders may accept lower scores with additional requirements. |
| Auto Loan | Credit score requirements for auto loans can vary, but a score of 660 or higher is typically considered good for securing favorable loan terms. |
| Personal Loan | Personal loans may have more flexible credit score requirements, but a score of 580 or higher is often recommended for better chances of approval. |
Loan Approval Criteria

When it comes to approving a loan, lenders consider a variety of criteria to assess the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan. Meeting these criteria is crucial for expediting the approval process and increasing the chances of getting the loan approved.
Factors Considered by Lenders
- Income and Employment Stability: Lenders look at the borrower’s income level and job stability to ensure they have the means to repay the loan.
- Credit History: A good credit history demonstrates the borrower’s ability to manage debt responsibly and increases the likelihood of loan approval.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lenders evaluate the borrower’s debt-to-income ratio to determine if they can afford to take on additional debt.
- Collateral: For secured loans, lenders may require collateral to reduce the risk, such as a car or property.
Factors Leading to Loan Rejection
- Low Credit Score: A low credit score indicates a higher risk for lenders, leading to rejection of the loan application.
- Insufficient Income: If the borrower’s income is not enough to cover the loan payments, the application may be denied.
- Poor Employment History: Unstable employment or frequent job changes can raise concerns for lenders.
- High Debt Levels: Excessive existing debt can signal financial strain and result in rejection of the loan.
Expedite Approval Process
- Provide Complete Documentation: Submitting all required documents accurately and promptly can speed up the approval process.
- Improve Credit Score: Working on improving the credit score before applying for a loan can increase the chances of approval.
- Choose Realistic Loan Amount: Applying for a loan amount within your means can make it easier for lenders to approve the application.
Verification Process
When applying for a loan, lenders go through a verification process to ensure the accuracy of the information provided by the borrower. This step is crucial in determining the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan.
Importance of Accurate Information
Providing accurate information during the verification process is vital as it helps lenders assess the borrower’s financial situation correctly. Any discrepancies or false information can lead to a denial of the loan application or even legal consequences for the borrower.
- Verification of Income: Lenders verify the borrower’s income by requesting pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements to ensure they can afford to repay the loan.
- Employment Verification: Lenders contact the borrower’s employer to confirm their job status and stability.
- Asset Verification: Lenders may verify the borrower’s assets, such as savings accounts or investments, to assess their overall financial health.
Common Verification Methods, Loan approval process
Lenders use various methods to verify the information provided by the borrower, including:
- Document Verification: Lenders review official documents, such as ID cards, bank statements, and pay stubs, to confirm the borrower’s identity and financial status.
- Credit Report Check: Lenders pull the borrower’s credit report to evaluate their credit history, outstanding debts, and payment behavior.
- Reference Checks: Lenders may contact references provided by the borrower, such as previous landlords or employers, to validate their character and reliability.